This week, we learned about carbohydrate. In this chapter, we looked into carbohydrates and concentrated specifically on sugar and their functions in food.
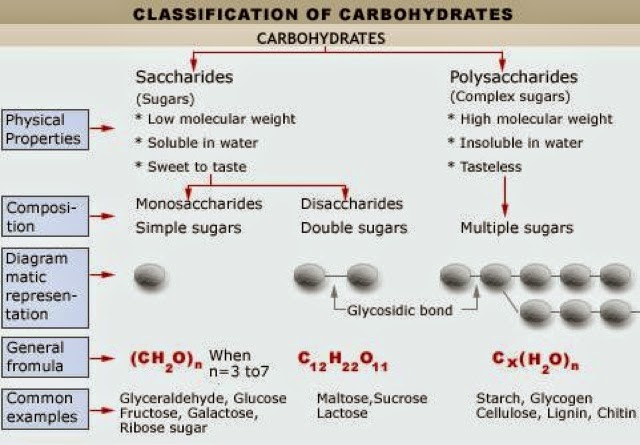
Carbohydrate can be devided into 2 categories which are saccharides and polysaccharides. Saccharides or sugar can be divided into 2 categories which are monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Monosaccharides is the simplest unit of carbohydrates, whereas disaccharides are 2 units of monosaccharides that are joined by glycosidic bond.
While polisaccharides are complex sugars made from multiple sugar molecule units that are joined by glycosidic bond.
Functions of sugar include:
Although the main reason for the use of sugar is its sweet taste, sugar has many other functions in food technology. The most important among these are that added sugar in foods acts as a sweetener, preservative, texture modifier, fermentation substrate, flavouring and colouring agent, bulking agent. The various methods of use of sugar are based on its physical and chemical properties. The replacement of sugar by the newly available sweeteners is difficult if the sweetness values or physical and chemical properties of the substitutes differ greatly from those of sucrose.